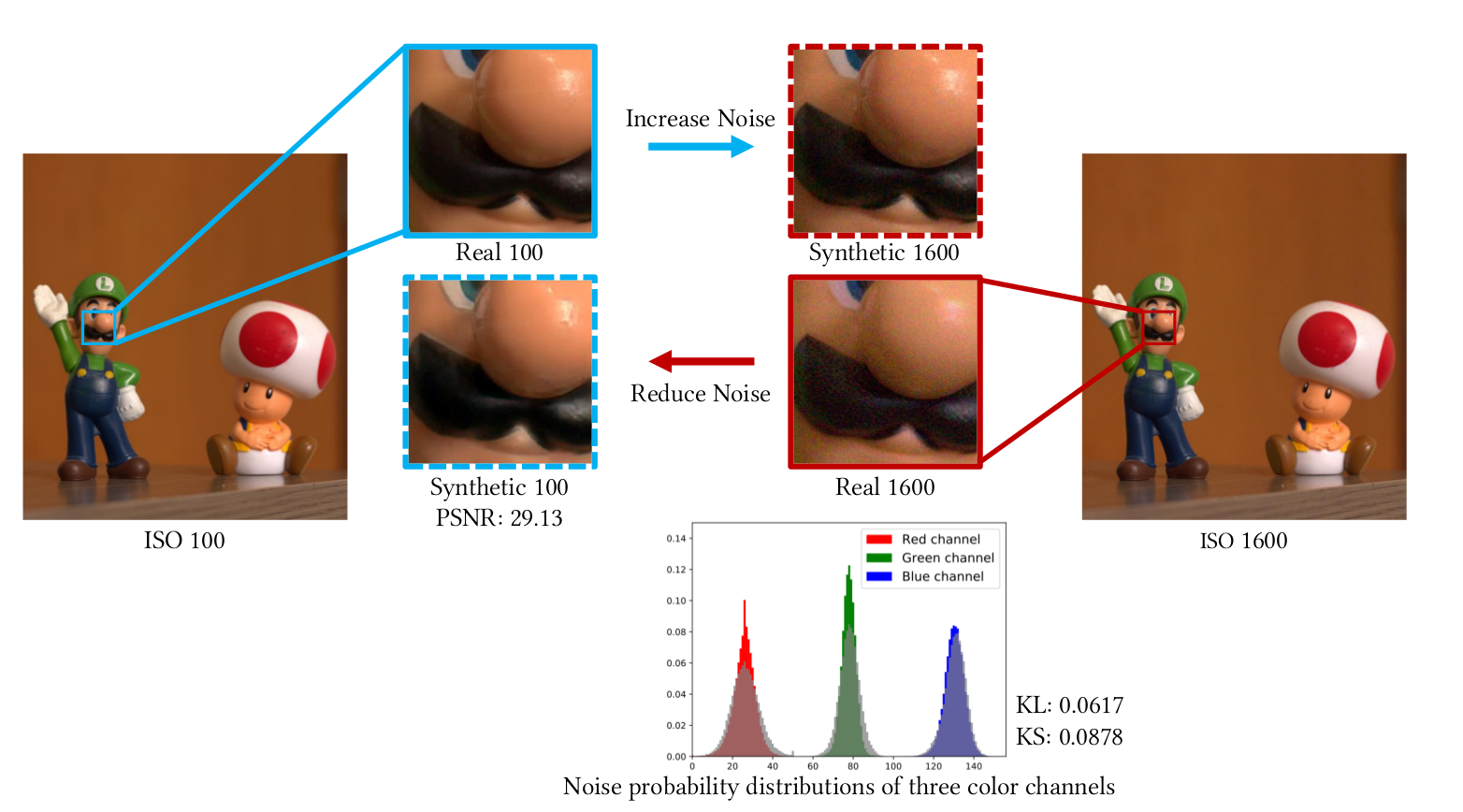
| Fig. 1. Using our technique to adjust the noise level of photographs to different ISO values. A photograph captured with ISO 100 (left) has its noise level adjusted to ISO 1600 (blue arrow). Likewise, another photograph of the same scene taken with ISO 1600 (right) has its noise level adjusted to ISO 100 (red arrow). The noise distributions for patches Real 1600 and Synthetic 1600 have a Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence of 0.0617 and the result of their Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test is 0.0878 (with a p-value of 7.81 × 10 −220 ), indicating that the two distributions are very similar. The red, green, and blue histograms underneath patch Real 1600 show the noise distributions corresponding to the R, G, and B channels of patch Real 1600, respectively. The superimposed gray histograms are the corresponding noise distributions for the patch Synthetic 1600. The PSNR value computed for patch Synthetic 100 is 29.13, also indicating a good agreement with patch Real 100. |
|
bhenz@inf.ufrgs.br |
eslgastal@inf.ufrgs.br |
oliveira@inf.ufrgs.br |





